Spoke 11: The Biblewheel and The 11th Century
Alexios I Komnenos and The Call For a Crusade
Alexios I Komnenos reigned until the early 12th Century. At the end of the 11th Century he successfully persuaded the West to join them to battle against the Turks, thus it was the beginning of the Crusades. Similarly Ahab the king of Israel persuaded Jehoshaphat king of Judah to fight against the Syrians. Jehoshaphat considered Judah and Israel to be as one and united people.
Since Alexios reigned from the end of the 11th Century to the beginning of the 12th, it reminds me of the 11th chapter of the 12th book 2Kings where the people along with the High Priest actually supported the coronation of the young Joash (seven years old) against the queen Athaliah. In this case, the 11th century, the people supported, along with the empress to adopt Alexios and his brother into her family to prepare them for royal duty:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alexios_I_Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos and The Call For a Crusade
Alexios I Komnenos reigned until the early 12th Century. At the end of the 11th Century he successfully persuaded the West to join them to battle against the Turks, thus it was the beginning of the Crusades. Similarly Ahab the king of Israel persuaded Jehoshaphat king of Judah to fight against the Syrians. Jehoshaphat considered Judah and Israel to be as one and united people.
Since Alexios reigned from the end of the 11th Century to the beginning of the 12th, it reminds me of the 11th chapter of the 12th book 2Kings where the people along with the High Priest actually supported the coronation of the young Joash (seven years old) against the queen Athaliah. In this case, the 11th century, the people supported, along with the empress to adopt Alexios and his brother into her family to prepare them for royal duty:
Alexios I Komnenos
| Alexios I Komnenos | |
|---|---|
| Emperor and Autocrat of the Romans | |

Portrait of Emperor Alexios I, from a Greek manuscript
| |
| Emperor of the Byzantine Empire | |
| Reign | 1 April 1081[1] – 15 August 1118 |
| Coronation | 5 April 1081[2] |
| Predecessor | Nikephoros III Botaneiates |
| Successor | John II Komnenos |
| Born | 1048 |
| Died | 15 August 1118 (age 70) |
| Spouse | Irene Doukaina |
| Issue | |
| Dynasty | Komnenoi |
| Father | John Komnenos |
| Mother | Anna Dalassene |
Alexios I Komnenos (Greek: Ἀλέξιος Αʹ Κομνηνός, c. 1048 – 15 August 1118) was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118. Although he was not the founder of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during his reign that the Komnenos family came to full power. Inheriting a collapsing empire and faced with constant warfare during his reign against both the Seljuq Turks in Asia Minor and the Normans in the western Balkans, Alexios was able to curb the Byzantine decline and begin the military, financial, and territorial recovery known as the Komnenian restoration. The basis for this recovery were various reforms initiated by Alexios. His appeals to Western Europe for help against the Turks were also the catalyst that likely contributed to the convoking of the Crusades.
Life
Alexios was the son of the Domestic of the Schools John Komnenos and Anna Dalassene,[3] and the nephew of Isaac I Komnenos (emperor 1057–1059). Alexios' father declined the throne on the abdication of Isaac, who was thus succeeded by four emperors of other families between 1059 and 1081. Under one of these emperors, Romanos IV Diogenes (1067–1071), Alexios served with distinction against the Seljuq Turks.[4] Under Michael VII Doukas Parapinakes (1071–1078) and Nikephoros III Botaneiates (1078–1081), he was also employed, along with his elder brother Isaac, against rebels in Asia Minor, Thrace, and in Epirus.[5]
In 1074, western mercenaries led by Roussel de Bailleul rebelled in Asia Minor,[6] but Alexios successfully subdued them by 1076.[7] In 1078, he was appointed commander of the field army in the West by Nikephoros III.[8] In this capacity, Alexios defeated the rebellions of Nikephoros Bryennios the Elder (whose son or grandson later married Alexios' daughter Anna) and Nikephoros Basilakes, the first at the Battle of Kalavrye and the latter in a surprise night attack on his camp.[9] Alexios was ordered to march against his brother-in-law Nikephoros Melissenos in Asia Minor but refused to fight his kinsman. This did not, however, lead to a demotion, as Alexios was needed to counter the expected invasion of the Normans of Southern Italy, led by Robert Guiscard.
Conspiracy and revolt of the Komnenoi against Botaneiates
While Byzantine troops were assembling for the expedition, the Doukas faction at court approached Alexios and convinced him to join a conspiracy against Nikephoros III. The mother of Alexios, Anna Dalassene, was to play a prominent role in this coup d'état of 1081, along with the current empress, Maria of Alania.[10] First married to Michael VII Doukas and secondly to Nikephoros III Botaneiates, she was preoccupied with the future of her son by Michael VII, Constantine Doukas. Nikephoros III intended to leave the throne to one of his close relatives,[11] and this resulted in Maria's ambivalence and alliance with the Komnenoi, though the real driving force behind this political alliance was Anna Dalassene.[12]
The empress was already closely connected to the Komnenoi through Maria's cousin Irene's marriage to Isaac Komnenos,[11] so the Komnenoi brothers were able to see her under the pretense of a friendly family visit. Furthermore, to aid the conspiracy Maria had adopted Alexios as her son, though she was only five years older than he.[13]Maria was persuaded to do so on the advice of her own "Alans" and her eunuchs, who had been instigated by Isaac Komnenos. Given Anna's tight hold on her family, Alexios must have been adopted with her implicit approval.[10] As a result, Alexios and Constantine, Maria's son, were now adoptive brothers, and both Isaac and Alexios took an oath that they would safeguard his rights as emperor.[14] By secretly giving inside information to the Komnenoi, Maria was an invaluable ally.[15]
As stated in the Alexiad, Isaac and Alexios left Constantinople in mid-February 1081 to raise an army against Botaneiates.[16]However, when the time came, Anna quickly and surreptitiously mobilized the remainder of the family and took refuge in the Hagia Sophia. From there she negotiated with the emperor for the safety of family members left in the capital, while protesting her sons' innocence of hostile actions. Under the falsehood of making a vesperal visit to worship at the church, she deliberately excluded the grandson of Botaneiates and his loyal tutor, met with Alexios and Isaac, and fled for the forum of Constantine.[10] The tutor discovered they were missing and eventually found them on the palace grounds, but Anna was able to convince him that they would return to the palace shortly. Then to gain entrance to both the outer and inner sanctuary of the church, the women pretended to the gatekeepers that they were pilgrims from Cappadocia who had spent all their funds and wanted to worship before starting their return trip. However, before they were to gain entry into the sanctuary, Straboromanos and royal guards caught up with them to summon them back to the palace.[10] Anna then protested that the family was in fear for their lives, her sons were loyal subjects (Alexios and Isaac were discovered absent without leave), and had learned of a plot by enemies of the Komnenoi to have them both blinded and had, therefore, fled the capital so they may continue to be of loyal service to the emperor.[17] She refused to go with them and demanded that they allow her to pray to the Mother of God for protection. This request was granted and Anna then manifested her true theatrical and manipulative capabilities:
Nikephoros III Botaneiates was forced into a public vow that he would grant protection to the family.[10] Straboromanos tried to give Anna his cross, but for her it was not sufficiently large enough for all bystanders to witness the oath. She also demanded that the cross be personally sent by Botaneiates as a vow of his good faith. He obliged, sending a complete assurance for the family with his own cross. At the emperor's further insistence, and for their own protection, they took refuge at the convent of Petrion, where they were eventually joined by Maria of Bulgaria, mother of Irene Doukaina.[10] Botaneiates allowed them to be treated as refugees rather than as guests. They were allowed to have family members bring in their own food and were on good terms with the guards from whom they learned the latest news.[19] Anna was highly successful in three important aspects of the revolt: she bought time for her sons to steal imperial horses from the stables and escape the city; she distracted the emperor, giving her sons time to gather and arm their troops; and she gave a false sense of security to Botaneiates that there was no real treasonous coup against him.[10] After bribing the Western troops guarding the city, Isaac and Alexios Komnenos entered the capital victoriously on April 1, 1081.[20]
During this time, Alexios was rumored to be the lover of Empress Maria of Alania, the daughter of King Bagrat IV of Georgia, who had been successively married to Michael VII Doukas and his successor Nikephoros III Botaneiates, and who was renowned for her beauty.[21] Alexios arranged for Maria to stay on the palace grounds, and it was thought that he was considering marrying her. However, his mother consolidated the Doukas family connection by arranging the Emperor's marriage to Irene Doukaina, granddaughter of the Caesar John Doukas, the uncle of Michael VII, who would not have supported Alexios otherwise. As a measure intended to keep the support of the Doukai, Alexios restored Constantine Doukas, the young son of Michael VII and Maria, as co-emperor[22] and a little later betrothed him to his own first-born daughter Anna, who moved into the Mangana Palace with her fiancé and his mother.
This situation changed drastically, however, when Alexios' first son John II Komnenos was born in 1087:[23] Anna's engagement to Constantine was dissolved, and she was moved to the main Palace to live with her mother and grandmother. Alexios became estranged from Maria, who was stripped of her imperial title and retired to a monastery, and Constantine Doukas was deprived of his status as co-emperor.[23] Nevertheless, he remained in good relations with the imperial family and succumbed to his weak constitution soon afterwards.
Wars against the Normans, Pechenegs, and Tzachas
The nearly thirty-seven year reign of Alexios was full of struggle. At the outset he faced the formidable attack of the Normans, led by Robert Guiscard and his son Bohemund, who took Dyrrhachium and Corfu and laid siege to Larissa in Thessaly[5] (see Battle of Dyrrhachium).[9] Alexios suffered several defeats before he was able to strike back with success. He enhanced his resistance by bribing the German king Henry IV with 360,000 gold pieces to attack the Normans in Italy,[24] which forced the Normans to concentrate on their defenses at home in 1083–84. He also secured the alliance of Henry, Count of Monte Sant'Angelo, who controlled the Gargano Peninsulaand dated his charters by Alexios' reign. Henry's allegiance would be the last example of Byzantine political control on peninsular Italy. The Norman danger subsided with the death of Guiscard in 1085, and the Byzantines recovered most of their losses.[25]
Alexios next had to deal with disturbances in Thrace, where the heretical sects of the Bogomils and the Paulicians revolted and made common cause with the Pechenegsfrom beyond the Danube.[26] Paulician soldiers in imperial service likewise deserted during Alexios' battles with the Normans.[27] As soon as the Norman threat had passed, Alexios set out to punish the rebels and deserters, confiscating their lands. This led to a further revolt near Philippopolis, and the commander of the field army in the west, Gregory Pakourianos, was defeated and killed in the ensuing battle. In 1087 the Pechenegs raided into Thrace, and Alexios crossed into Moesia to retaliate but failed to take Dorostolon (Silistra).[28] During his retreat, the emperor was surrounded and worn down by the Pechenegs, who forced him to sign a truce and to pay protection money. In 1090 the Pechenegs invaded Thrace again,[29] while Tzachas, the brother-in-law of the Sultan of Rum, launched a fleet and attempted to arrange a joint siege of Constantinople with the Pechenegs.[30] Alexios overcame this crisis by entering into an alliance with a horde of 40,000 Cumans, with whose help he crushed the Pechenegs at Levounion in Thrace on 29 April 1091.[31]
This put an end to the Pecheneg threat, but in 1094 the Cumans began to raid the imperial territories in the Balkans. Led by a pretender claiming to be Constantine Diogenes, a long-dead son of the Emperor Romanos IV,[32] the Cumans crossed the mountains and raided into eastern Thrace until their leader was eliminated at Adrianople. With the Balkans more or less pacified, Alexios could now turn his attention to Asia Minor, which had been almost completely overrun by the Seljuq Turks.[33]
Byzantine-Seljuq Wars and the First Crusade
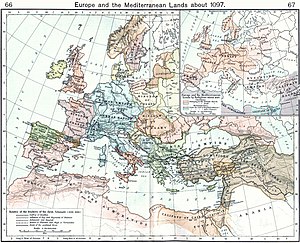
By the time Alexios ascended the throne, the Seljuqs had taken most of Asia Minor. Alexios was able to secure much of the coastal regions by sending peasant soldiers to raid the Seljuq camps, but these victories were unable to stop the Turks altogether.[34] As early as 1090, Alexios had taken reconciliatory measures towards the Papacy,[35] with the intention of seeking western support against the Seljuqs. In 1095 his ambassadors appeared before Pope Urban II at the Council of Piacenza.[36] The help he sought from the West was simply some mercenary forces, not the immense hosts that arrived, to his consternation and embarrassment, after the pope preached the First Crusade at the Council of Clermont later that same year.[37] Not quite ready to supply this number of people as they traversed his territories, the emperor saw his Balkan possessions subjected to further pillage at the hands of his own allies.[38] Alexios dealt with the first disorganized group of Crusaders, led by the preacher Peter the Hermit, by sending them on to Asia Minor, where they were massacred by the Turks in 1096.[39]
The second and much more formidable host of crusaders gradually made its way to Constantinople, led in sections by Godfrey of Bouillon, Bohemond of Taranto, Raymond IV of Toulouse, and other important members of the western nobility.[40] Alexios used the opportunity to meet the crusader leaders separately as they arrived, extracting from them oaths of homage and the promise to turn over conquered lands to the Byzantine Empire.[41] Transferring each contingent into Asia, Alexios promised to supply them with provisions in return for their oaths of homage. The crusade was a notable success for Byzantium, as Alexios recovered a number of important cities and islands. The siege of Nicaea by the crusaders forced the city to surrender to the emperor in 1097, and the subsequent crusader victory at Dorylaion allowed the Byzantine forces to recover much of western Asia Minor.[42] John Doukas re-established Byzantine rule in Chios, Rhodes, Smyrna, Ephesus, Sardis, and Philadelphia in 1097–1099. This success is ascribed by Alexios' daughter Anna to his policy and diplomacy, but by the Latin historians of the crusade to his treachery and deception.[5] In 1099, a Byzantine fleet of ten ships was sent to assist the crusaders in capturing Laodicea and other coastal towns as far as Tripoli. The crusaders believed their oaths were made invalid when the Byzantine contingent under Tatikios failed to help them during the siege of Antioch;[36] Bohemund, who had set himself up as Prince of Antioch,[42] briefly went to war with Alexios in the Balkans, but he was blockaded by the Byzantine forces and agreed to become a vassal of Alexios by the Treaty of Devol in 1108.[43]
In 1116, though already terminally ill, Alexios conducted a series of defensive operations in Bythinia and Mysia to defend his Anatolian territories against the inroads of Malik Shah, the Seljuq Sultan of Iconium. In 1117 he moved onto the offensive and pushed his army deep into the Turkish-dominated Anatolian Plateau, where he defeated the Seljuq sultan at the Battle of Philomelion.[44]
Personal life
During the last twenty years of his life Alexios lost much of his popularity.[45] The years were marked by persecution of the followers of the Paulician and Bogomilheresies[46]—one of his last acts was to publicly burn at the stake Basil, a Bogomil leader, with whom he had engaged in a theological dispute.[5][39] In spite of the success of the First Crusade, Alexios also had to repel numerous attempts on his territory by the Seljuqs in 1110–1117.[47]
Alexios was for many years under the strong influence of an eminence grise, his mother Anna Dalassene, a wise and immensely able politician whom, in a uniquely irregular fashion, he had crowned as Augusta instead of the rightful claimant to the title, his wife Irene Doukaina.[48] Dalassene was the effective administrator of the Empire during Alexios' long absences in military campaigns: she was constantly at odds with her daughter-in-law and had assumed total responsibility for the upbringing and education of her granddaughter Anna Komnene.
Succession
Alexios' last years were also troubled by anxieties over the succession. Although he had crowned his son John II Komnenos co-emperor at the age of five in 1092, his wife, Irene Doukaina wished to alter the succession in favor of their daughter Anna and Anna's husband, Nikephoros Bryennios the Younger.[49] Bryennios had been made kaisar (Caesar) and received the newly created title of panhypersebastos ("honoured above all"), and remained loyal to both Alexios and John. Nevertheless, the intrigues of Irene and Anna disturbed even Alexios' dying hours.[36]
Pretenders and rebels
Apart from all of his external enemies, a host of rebels also sought to overthrow Alexios from the imperial throne, thereby posing another major threat to his reign.[39] Due to the troubled times the empire was enduring, he had by far the greatest number of rebellions against him of all the Byzantine emperors.[50] These included:
Pre First Crusade
- Raictor, a Byzantine monk who claimed to be the emperor Michael VII. He presented himself to Robert Guiscard who used him as a pretext to launch his invasion of the Byzantine Empire.[50]
- A conspiracy in 1084 involving several senators and officers of the army. This was uncovered before too many followers were enlisted. In order to conceal the importance of the conspiracy, Alexios merely banished the wealthiest plotters and confiscated their estates.[50]
- Tzachas, a Seljuq Turkic emir who assumed the title of emperor in 1092.[51]
- Constantine Humbertopoulos, who had assisted Alexios in gaining the throne in 1081 conspired against him in 1091 with an Armenian called Ariebes.[51]
- John Komnenos, Alexios' nephew, governor of Dyrrachium, accused of a conspiracy by Theophylact of Bulgaria.[51]
- Theodore Gabras, the quasi-independent governor of Trebizond and his son Gregory.[51]
- Michael Taronites, the brother-in-law of Alexios.[51]
- Nikephoros Diogenes, the son of emperor Romanos IV.[51]
- Pseudo-Diogenes, an impostor who assumed the identity of another of Romanos' sons, Leo Diogenes.[52]
- Karykes, the leader of a revolt in Crete.[51]
- Rhapsomates, who tried to create an independent kingdom in Cyprus.[51]
Post First Crusade
- Salomon, a senator of great wealth who in 1106 engaged in a plot with four brothers of the Anemas family.[53]
- Gregory Taronites, another governor of Trebizond.[53]
- The illegitimate descendant of a Bulgarian prince named Aron formed a plot in 1107 to murder Alexios as he was encamped near Thessalonica. The presence of the empress Irene and her attendants, however, made the execution of the plot difficult. In an attempt to have her return to Constantinople, the conspirators produced pamphlets that mocked and slandered the empress, and left them in her tent. A search for the author of the publications uncovered the whole plot, yet Aron was only banished due to his connection of the royal line of Bulgaria, whose blood also flowed in the veins of the empress Irene.[54]
Reform of the monetary system
Under Alexios the debased solidus (tetarteron and histamenon) was discontinued and a gold coinage of higher fineness (generally .900–.950) was established in 1092, commonly called the hyperpyron at 4.45 grs. The hyperpyron was slightly smaller than the solidus.
It was introduced along with the electrum aspron trachy worth a third of a hyperpyron and about 25% gold and 75% silver, the billonaspron trachy or stamenon,[55] valued at 48 to the hyperpyron and with 7% silver wash and the copper tetarteron and noummionworth 18 and 36 to the billon aspron trachy.[56]
Alexios' reform of the Byzantine monetary system was an important basis for the financial recovery and therefore supported the so-called Komnenian restoration, as the new coinage restored financial confidence.
Legacy
Alexios I had overcome a dangerous crisis and stabilized the Byzantine Empire, inaugurating a century of imperial prosperity and success.[49] He had also profoundly altered the nature of the Byzantine government.[57] By seeking close alliances with powerful noble families, Alexios put an end to the tradition of imperial exclusivity and co-opted most of the nobility into his extended family and, through it, his government. Those who did not become part of this extended family were deprived of power and prestige.[39] This measure, which was intended to diminish opposition, was paralleled by the introduction of new courtly dignities, like that of panhypersebastos given to Nikephoros Bryennios, or that of sebastokrator given to the emperor's brother Isaac Komnenos.[57] Although this policy met with initial success, it gradually undermined the relative effectiveness of imperial bureaucracy by placing family connections over merit. Alexios' policy of integration of the nobility bore the fruit of continuity: every Byzantine emperor who reigned after Alexios I Komnenos was related to him by either descent or marriage.
Family
By his marriage with Irene Doukaina, Alexios I had the following children:[58]
- Anna Komnene, who married the Caesar Nikephoros Bryennios the Younger.
- Maria Komnene, who married (1) Gregory Gabras and (2) Nikephoros Katakalon.
- John II Komnenos, who succeeded as emperor.
- Andronikos Komnenos, who died circa 1117 battling Turks[59], sebastokrator.
- Isaac Komnenos, sebastokrator.
- Eudokia Komnene, who married the son of Constantine Iasites.
- Theodora Komnene, who married (1) Constantine Kourtikes and (2) Constantine Angelos. By him she was the grandmother of Emperors Isaac II Angelos and Alexios III Angelos, as well as the progenitor of the ruling dynasty of the Despotate of Epirus.
- Manuel Komnenos, born February 1097 and known only from a manuscript now in Moscow, died probably soon after his birth[60]
- Zoe Komnene, born March 1098 and known only from a manuscript now in Moscow, died probably soon after her birth[60]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alexios_I_Komnenos
Comparing 1Kings the 11th Book
with the 11th Century
| |
|---|---|
1Kings 20 - Listen
1 And Benhadad the king of Syria gathered all his host together: and [there were] thirty and two kings with him, and horses, and chariots: and he went up and besieged Samaria, and warred against it. 2 And he sent messengers to Ahab king of Israel into the city, and said unto him, Thus saith Benhadad, 3 Thy silver and thy gold [is] mine; thy wives also and thy children, [even] the goodliest, [are] mine. 4 And the king of Israel answered and said, My lord, O king, according to thy saying, I [am] thine, and all that I have. 5 And the messengers came again, and said, Thus speaketh Benhadad, saying, Although I have sent unto thee, saying, Thou shalt deliver me thy silver, and thy gold, and thy wives, and thy children; 6 Yet I will send my servants unto thee to morrow about this time, and they shall search thine house, and the houses of thy servants; and it shall be, [that] whatsoever is pleasant in thine eyes, they shall put [it] in their hand, and take [it] away. 7 Then the king of Israel called all the elders of the land, and said, Mark, I pray you, and see how this [man] seeketh mischief: for he sent unto me for my wives, and for my children, and for my silver, and for my gold; and I denied him not. 8 And all the elders and all the people said unto him, Hearken not [unto him], nor consent. 9 Wherefore he said unto the messengers of Benhadad, Tell my lord the king, All that thou didst send for to thy servant at the first I will do: but this thing I may not do. And the messengers departed, and brought him word again. 10 And Benhadad sent unto him, and said, The gods do so unto me, and more also, if the dust of Samaria shall suffice for handfuls for all the people that follow me. 11 And the king of Israel answered and said, Tell [him], Let not him that girdeth on [his harness] boast himself as he that putteth it off. 12 And it came to pass, when [Benhadad] heard this message, as he [was] drinking, he and the kings in the pavilions, that he said unto his servants, Set [yourselves in array]. And they set [themselves in array] against the city. 13 And, behold, there came a prophet unto Ahab king of Israel, saying, Thus saith the LORD, Hast thou seen all this great multitude? behold, I will deliver it into thine hand this day; and thou shalt know that I [am] the LORD. 14 And Ahab said, By whom? And he said, Thus saith the LORD, [Even] by the young men of the princes of the provinces. Then he said, Who shall order the battle? And he answered, Thou. 15 Then he numbered the young men of the princes of the provinces, and they were two hundred and thirty two: and after them he numbered all the people, [even] all the children of Israel, [being] seven thousand. 16 And they went out at noon. But Benhadad [was] drinking himself drunk in the pavilions, he and the kings, the thirty and two kings that helped him. 17 And the young men of the princes of the provinces went out first; and Benhadad sent out, and they told him, saying, There are men come out of Samaria. 18 And he said, Whether they be come out for peace, take them alive; or whether they be come out for war, take them alive. 19 So these young men of the princes of the provinces came out of the city, and the army which followed them. 20 And they slew every one his man: and the Syrians fled; and Israel pursued them: and Benhadad the king of Syria escaped on an horse with the horsemen. 21 And the king of Israel went out, and smote the horses and chariots, and slew the Syrians with a great slaughter. 22 And the prophet came to the king of Israel, and said unto him, Go, strengthen thyself, and mark, and see what thou doest: for at the return of the year the king of Syria will come up against thee. 23 And the servants of the king of Syria said unto him, Their gods [are] gods of the hills; therefore they were stronger than we; but let us fight against them in the plain, and surely we shall be stronger than they. 24 And do this thing, Take the kings away, every man out of his place, and put captains in their rooms: 25 And number thee an army, like the army that thou hast lost, horse for horse, and chariot for chariot: and we will fight against them in the plain, [and] surely we shall be stronger than they. And he hearkened unto their voice, and did so. 26 And it came to pass at the return of the year, that Benhadad numbered the Syrians, and went up to Aphek, to fight against Israel. 27 And the children of Israel were numbered, and were all present, and went against them: and the children of Israel pitched before them like two little flocks of kids; but the Syrians filled the country. 28 And there came a man of God, and spake unto the king of Israel, and said, Thus saith the LORD, Because the Syrians have said, The LORD [is] God of the hills, but he [is] not God of the valleys, therefore will I deliver all this great multitude into thine hand, and ye shall know that I [am] the LORD. 29 And they pitched one over against the other seven days. And [so] it was, that in the seventh day the battle was joined: and the children of Israel slew of the Syrians an hundred thousand footmen in one day. 30 But the rest fled to Aphek, into the city; and [there] a wall fell upon twenty and seven thousand of the men [that were] left. And Benhadad fled, and came into the city, into an inner chamber. 31 And his servants said unto him, Behold now, we have heard that the kings of the house of Israel [are] merciful kings: let us, I pray thee, put sackcloth on our loins, and ropes upon our heads, and go out to the king of Israel: peradventure he will save thy life. 32 So they girded sackcloth on their loins, and [put] ropes on their heads, and came to the king of Israel, and said, Thy servant Benhadad saith, I pray thee, let me live. And he said, [Is] he yet alive? he [is] my brother. 33 Now the men did diligently observe whether [any thing would come] from him, and did hastily catch [it]: and they said, Thy brother Benhadad. Then he said, Go ye, bring him. Then Benhadad came forth to him; and he caused him to come up into the chariot. 34 And [Benhadad] said unto him, The cities, which my father took from thy father, I will restore; and thou shalt make streets for thee in Damascus, as my father made in Samaria. Then [said Ahab], I will send thee away with this covenant. So he made a covenant with him, and sent him away. 35 And a certain man of the sons of the prophets said unto his neighbour in the word of the LORD, Smite me, I pray thee. And the man refused to smite him. 36 Then said he unto him, Because thou hast not obeyed the voice of the LORD, behold, as soon as thou art departed from me, a lion shall slay thee. And as soon as he was departed from him, a lion found him, and slew him. 37 Then he found another man, and said, Smite me, I pray thee. And the man smote him, so that in smiting he wounded [him]. 38 So the prophet departed, and waited for the king by the way, and disguised himself with ashes upon his face. 39 And as the king passed by, he cried unto the king: and he said, Thy servant went out into the midst of the battle; and, behold, a man turned aside, and brought a man unto me, and said, Keep this man: if by any means he be missing, then shall thy life be for his life, or else thou shalt pay a talent of silver. 40 And as thy servant was busy here and there, he was gone. And the king of Israel said unto him, So [shall] thy judgment [be]; thyself hast decided [it]. 41 And he hasted, and took the ashes away from his face; and the king of Israel discerned him that he [was] of the prophets. 42 And he said unto him, Thus saith the LORD, Because thou hast let go out of [thy] hand a man whom I appointed to utter destruction, therefore thy life shall go for his life, and thy people for his people. 43 And the king of Israel went to his house heavy and displeased, and came to Samaria. | |
Comparing 1Kings the 11th Book
with the 11th Century
| |
|---|---|
1Kings 22 - Listen
1 And they continued three years without war between Syria and Israel. 2 And it came to pass in the third year, that Jehoshaphat the king of Judah came down to the king of Israel. 3 And the king of Israel said unto his servants, Know ye that Ramoth in Gilead [is] ours, and we [be] still, [and] take it not out of the hand of the king of Syria? 4 And he said unto Jehoshaphat, Wilt thou go with me to battle to Ramothgilead? And Jehoshaphat said to the king of Israel, I [am] as thou [art], my people as thy people, my horses as thy horses. 5 And Jehoshaphat said unto the king of Israel, Enquire, I pray thee, at the word of the LORD to day. 6 Then the king of Israel gathered the prophets together, about four hundred men, and said unto them, Shall I go against Ramothgilead to battle, or shall I forbear? And they said, Go up; for the Lord shall deliver [it] into the hand of the king. 7 And Jehoshaphat said, [Is there] not here a prophet of the LORD besides, that we might enquire of him? 8 And the king of Israel said unto Jehoshaphat, [There is] yet one man, Micaiah the son of Imlah, by whom we may enquire of the LORD: but I hate him; for he doth not prophesy good concerning me, but evil. And Jehoshaphat said, Let not the king say so. 9 Then the king of Israel called an officer, and said, Hasten [hither] Micaiah the son of Imlah. 10 And the king of Israel and Jehoshaphat the king of Judah sat each on his throne, having put on their robes, in a void place in the entrance of the gate of Samaria; and all the prophets prophesied before them. 11 And Zedekiah the son of Chenaanah made him horns of iron: and he said, Thus saith the LORD, With these shalt thou push the Syrians, until thou have consumed them. 12 And all the prophets prophesied so, saying, Go up to Ramothgilead, and prosper: for the LORD shall deliver [it] into the king's hand. 13 And the messenger that was gone to call Micaiah spake unto him, saying, Behold now, the words of the prophets [declare] good unto the king with one mouth: let thy word, I pray thee, be like the word of one of them, and speak [that which is] good. 14 And Micaiah said, [As] the LORD liveth, what the LORD saith unto me, that will I speak. 15 So he came to the king. And the king said unto him, Micaiah, shall we go against Ramothgilead to battle, or shall we forbear? And he answered him, Go, and prosper: for the LORD shall deliver [it] into the hand of the king. 16 And the king said unto him, How many times shall I adjure thee that thou tell me nothing but [that which is] true in the name of the LORD? 17 And he said, I saw all Israel scattered upon the hills, as sheep that have not a shepherd: and the LORD said, These have no master: let them return every man to his house in peace. 18 And the king of Israel said unto Jehoshaphat, Did I not tell thee that he would prophesy no good concerning me, but evil? 19 And he said, Hear thou therefore the word of the LORD: I saw the LORD sitting on his throne, and all the host of heaven standing by him on his right hand and on his left. 20 And the LORD said, Who shall persuade Ahab, that he may go up and fall at Ramothgilead? And one said on this manner, and another said on that manner. 21 And there came forth a spirit, and stood before the LORD, and said, I will persuade him. 22 And the LORD said unto him, Wherewith? And he said, I will go forth, and I will be a lying spirit in the mouth of all his prophets. And he said, Thou shalt persuade [him], and prevail also: go forth, and do so. 23 Now therefore, behold, the LORD hath put a lying spirit in the mouth of all these thy prophets, and the LORD hath spoken evil concerning thee. 24 But Zedekiah the son of Chenaanah went near, and smote Micaiah on the cheek, and said, Which way went the Spirit of the LORD from me to speak unto thee? 25 And Micaiah said, Behold, thou shalt see in that day, when thou shalt go into an inner chamber to hide thyself. 26 And the king of Israel said, Take Micaiah, and carry him back unto Amon the governor of the city, and to Joash the king's son; 27 And say, Thus saith the king, Put this [fellow] in the prison, and feed him with bread of affliction and with water of affliction, until I come in peace. 28 And Micaiah said, If thou return at all in peace, the LORD hath not spoken by me. And he said, Hearken, O people, every one of you. 29 So the king of Israel and Jehoshaphat the king of Judah went up to Ramothgilead. 30 And the king of Israel said unto Jehoshaphat, I will disguise myself, and enter into the battle; but put thou on thy robes. And the king of Israel disguised himself, and went into the battle. 31 But the king of Syria commanded his thirty and two captains that had rule over his chariots, saying, Fight neither with small nor great, save only with the king of Israel. 32 And it came to pass, when the captains of the chariots saw Jehoshaphat, that they said, Surely it [is] the king of Israel. And they turned aside to fight against him: and Jehoshaphat cried out. 33 And it came to pass, when the captains of the chariots perceived that it [was] not the king of Israel, that they turned back from pursuing him. 34 And a [certain] man drew a bow at a venture, and smote the king of Israel between the joints of the harness: wherefore he said unto the driver of his chariot, Turn thine hand, and carry me out of the host; for I am wounded. 35 And the battle increased that day: and the king was stayed up in his chariot against the Syrians, and died at even: and the blood ran out of the wound into the midst of the chariot. 36 And there went a proclamation throughout the host about the going down of the sun, saying, Every man to his city, and every man to his own country. 37 So the king died, and was brought to Samaria; and they buried the king in Samaria. 38 And [one] washed the chariot in the pool of Samaria; and the dogs licked up his blood; and they washed his armour; according unto the word of the LORD which he spake. 39 Now the rest of the acts of Ahab, and all that he did, and the ivory house which he made, and all the cities that he built, [are] they not written in the book of the chronicles of the kings of Israel? 40 So Ahab slept with his fathers; and Ahaziah his son reigned in his stead. 41 And Jehoshaphat the son of Asa began to reign over Judah in the fourth year of Ahab king of Israel. 42 Jehoshaphat [was] thirty and five years old when he began to reign; and he reigned twenty and five years in Jerusalem. And his mother's name [was] Azubah the daughter of Shilhi. 43 And he walked in all the ways of Asa his father; he turned not aside from it, doing [that which was] right in the eyes of the LORD: nevertheless the high places were not taken away; [for] the people offered and burnt incense yet in the high places. 44 And Jehoshaphat made peace with the king of Israel. 45 Now the rest of the acts of Jehoshaphat, and his might that he shewed, and how he warred, [are] they not written in the book of the chronicles of the kings of Judah? 46 And the remnant of the sodomites, which remained in the days of his father Asa, he took out of the land. 47 [There was] then no king in Edom: a deputy [was] king. 48 Jehoshaphat made ships of Tharshish to go to Ophir for gold: but they went not; for the ships were broken at Eziongeber. 49 Then said Ahaziah the son of Ahab unto Jehoshaphat, Let my servants go with thy servants in the ships. But Jehoshaphat would not. 50 And Jehoshaphat slept with his fathers, and was buried with his fathers in the city of David his father: and Jehoram his son reigned in his stead. 51 Ahaziah the son of Ahab began to reign over Israel in Samaria the seventeenth year of Jehoshaphat king of Judah, and reigned two years over Israel. 52 And he did evil in the sight of the LORD, and walked in the way of his father, and in the way of his mother, and in the way of Jeroboam the son of Nebat, who made Israel to sin: 53 For he served Baal, and worshipped him, and provoked to anger the LORD God of Israel, according to all that his father had done. | |
| Comparing 2Kings 11 (12:11) with the 11th and 12th Centuries |
|
|---|---|
| 2Kings 11 - Listen 1 And when Athaliah the mother of Ahaziah saw that her son was dead, she arose and destroyed all the seed royal. 2 But Jehosheba, the daughter of king Joram, sister of Ahaziah, took Joash the son of Ahaziah, and stole him from among the king's sons [which were] slain; and they hid him, [even] him and his nurse, in the bedchamber from Athaliah, so that he was not slain. 3 And he was with her hid in the house of the LORD six years. And Athaliah did reign over the land. 4 And the seventh year Jehoiada sent and fetched the rulers over hundreds, with the captains and the guard, and brought them to him into the house of the LORD, and made a covenant with them, and took an oath of them in the house of the LORD, and shewed them the king's son. 5 And he commanded them, saying, This [is] the thing that ye shall do; A third part of you that enter in on the sabbath shall even be keepers of the watch of the king's house; 6 And a third part [shall be] at the gate of Sur; and a third part at the gate behind the guard: so shall ye keep the watch of the house, that it be not broken down. 7 And two parts of all you that go forth on the sabbath, even they shall keep the watch of the house of the LORD about the king. 8 And ye shall compass the king round about, every man with his weapons in his hand: and he that cometh within the ranges, let him be slain: and be ye with the king as he goeth out and as he cometh in. 9 And the captains over the hundreds did according to all [things] that Jehoiada the priest commanded: and they took every man his men that were to come in on the sabbath, with them that should go out on the sabbath, and came to Jehoiada the priest. 10 And to the captains over hundreds did the priest give king David's spears and shields, that [were] in the temple of the LORD. 11 And the guard stood, every man with his weapons in his hand, round about the king, from the right corner of the temple to the left corner of the temple, [along] by the altar and the temple. 12 And he brought forth the king's son, and put the crown upon him, and [gave him] the testimony; and they made him king, and anointed him; and they clapped their hands, and said, God save the king. 13 And when Athaliah heard the noise of the guard [and] of the people, she came to the people into the temple of the LORD. 14 And when she looked, behold, the king stood by a pillar, as the manner [was], and the princes and the trumpeters by the king, and all the people of the land rejoiced, and blew with trumpets: and Athaliah rent her clothes, and cried, Treason, Treason. 15 But Jehoiada the priest commanded the captains of the hundreds, the officers of the host, and said unto them, Have her forth without the ranges: and him that followeth her kill with the sword. For the priest had said, Let her not be slain in the house of the LORD. 16 And they laid hands on her; and she went by the way by the which the horses came into the king's house: and there was she slain. 17 And Jehoiada made a covenant between the LORD and the king and the people, that they should be the LORD'S people; between the king also and the people. 18 And all the people of the land went into the house of Baal, and brake it down; his altars and his images brake they in pieces thoroughly, and slew Mattan the priest of Baal before the altars. And the priest appointed officers over the house of the LORD. 19 And he took the rulers over hundreds, and the captains, and the guard, and all the people of the land; and they brought down the king from the house of the LORD, and came by the way of the gate of the guard to the king's house. And he sat on the throne of the kings. 20 And all the people of the land rejoiced, and the city was in quiet: and they slew Athaliah with the sword [beside] the king's house. 21 Seven years old [was] Jehoash when he began to reign. |
|
![Biblewheel: A wise king scattereth the wicked, and bringeth the wheel over them. [Pro 20:26 KJV]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgiFT6-YCyrSoMjVlsXjQIWJVHaMXsChgqmAIk9mLeNmsgqWXD94k5TOPejvnORdnQ39OL3U4FleKWbC1r46q2t5nYnipb_qDZFNHQR_YXesnm6ucYt2g1DjbBhXnZmML3IHhunsYSeRBU/s1600-r/biblewheel_traced_edited.png)




No comments:
Post a Comment